ELVENTO provides the simplest solutions for the most complex problems
Being a trusted software development company in India, we employ industry best practices to deliver robust, secure & scalable custom software development services for the Mobile-First World

With over 5 years of experience, we deliver perfect products that can exceed your expectations.
Why Elvento Labs?

Startup Thinking
Nimble, agile, and proactive. Being a start-up ourselves, we know what it takes to constantly deliver our best.
Partner Approach
We are successful if our customer is successful. We don’t think of ourselves as a service provider but your technology partner and are driven by your success.
Product Mindset
We try to INSPIRE and AWAKEN people to the legendary being they were always meant to be. By providing tools and technology we aim to change the world, by changing the way you think.
Experience Design Thinking
Ease of use, correct information flow, exceptional experience, and conversion are the core of our UX methodology.
Hiring Philosophy
We hire the best so that our clients don't suffer. Our top professional teams need the least help to deliver flawless products.
Certified Teams and Company
Our professional teams are not only experienced in their respective technologies but also certified.
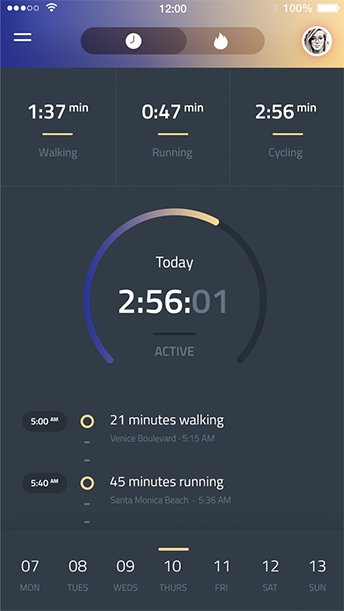
Mobile app development
Apps are redefining the way we interact with services and empowering businesses to engage with their customers
Web app development
Single-page applications are fast replacing dynamic websites with web apps so are the technology used to built them.
Desktop app development
We work with the best resources and team to meet your needs for the development of QT applications on Windows/Mac/Linux.
What our clients say about us
WHY CHOOSE US?
We have a dedicated and skilled development team which can easily be integrated with your in-house team or work as a separate extension to your business:
Our Track Record
We have been delivering excellent services since 2016. With over 20 cutting edge projects spread across multiple industries, we are a talented team to handle your job. We will be delighted to discuss your idea in detail.
Quality Driven Team
We have a unique system in place to ensure quality assurance for all projects. Our team tests and adopts the latest technologies to ensure our work is of the highest quality. Our job is to present a flawless end product to you.
Attention to Detail
Our processes only begin when we have accurately understood your ideas and expectations. What’s more, we send you updates about the latest functions and technology that can be added to improve your project.
Transparency
We believe in maintaining a long-term relationship with you. This is why we provide transparency in every aspect of our process. We will provide you daily or weekly updates during project's lifecycle so that you are always in the loop of what is the current progress.
Extensive Experience
We have been able to achieve winning solutions because our team members are experienced and highly skilled. Your ideas will be turned to reality by the masterminds and professional developers whose passion and knowledge in the field of Angular is exceptional.
Competitive Pricing
Our Web Development services are competitively priced to ensure you get high-quality at a reasonable fee. We leverage efficiency and access to the best resources to offer you a price within your budget and delivery of the completed job in your preferred timeline.
Blog
Check our latest posts
Let us know how we can help